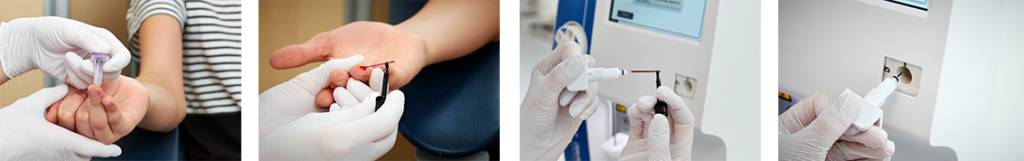
Boule hematology analyzers equipped with the micro-pipet adapter (MPA) inlet allows for CBC testing from a capillary blood sample taken directly from the patient – no excess blood collection, no vacuum tubes, or mixing required. To ensure agreement of the MPA method with other inlets, there are some things to consider to get your CBC testing from capillary blood right.

Benefits of capillary blood collection
Capillary blood sampling for direct CBC analysis is preferred in many cases. For example, collection of capillary blood can help overcome many of the pre-analytical errors associated with venous blood collection in vacuum tubes, including blood clotting or hemolysis as well as erroneous labelling or incorrect tube filling. Blood sampling from a fingerstick or heel-prick is many times considered less invasive to the patient and easer to perform for the healthcare professional. In blood donor assessment, CBC testing from a finger-stick blood sample saves the vein for the blood donation. To ensure agreement between CBC results from capillary blood and venous blood, there are some pre-analytical factors that should be considered to avoid discrepancies between parameter values.
Capillary sample blood collection procedure
Boule hematology analyzers have been calibrated prior to shipment. However, good laboratory practices dictate regular control of measured parameters. Any discrepancy between the MPA and open tube inlets should be adjusted by a recalibration.